
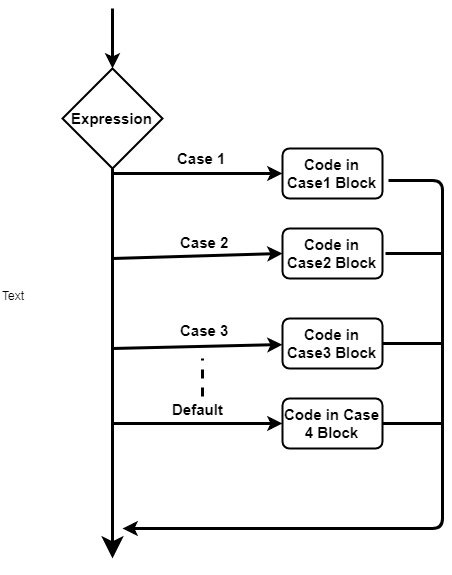
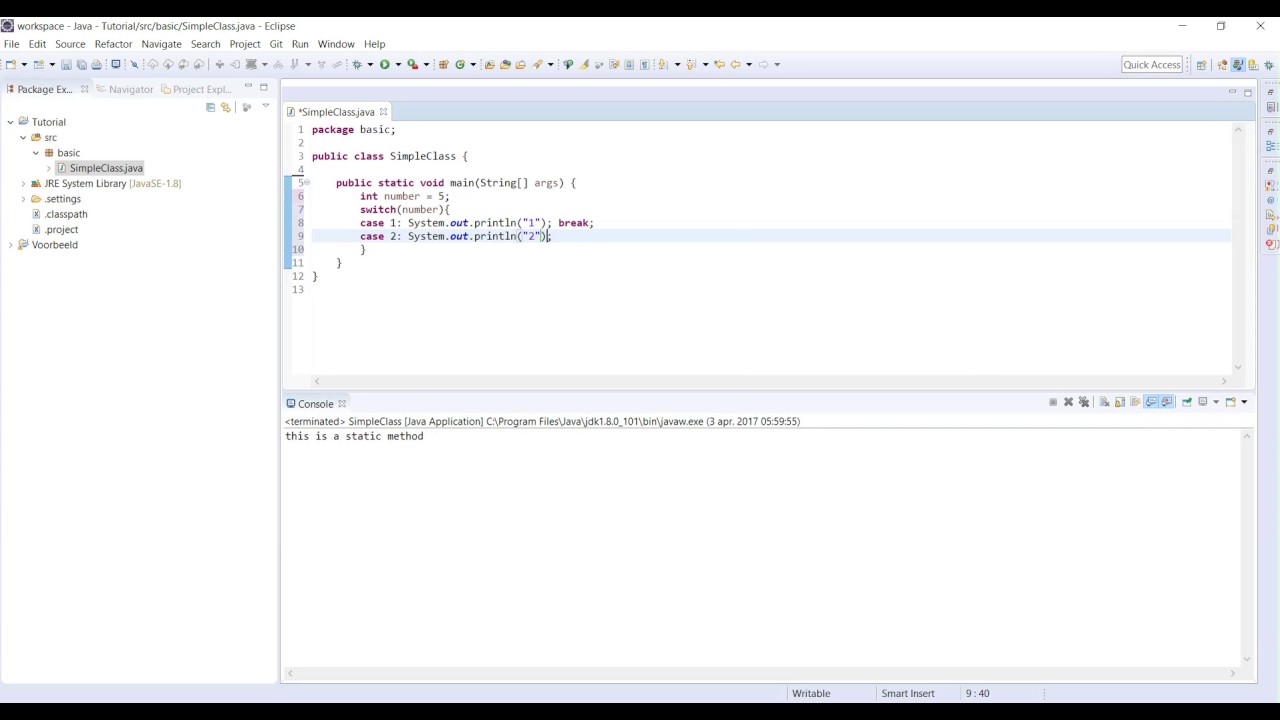
The default statement is optional and there is no need to use a break statement within it.it is not mandatory to provide a break statement for a case. It is up to Java 17 that it is available in a stable long support (LTS) release. The break statement within the case is optional i.e. It is important to note that switch expressions have been in the language since previous versions of Java, starting in Java 12 in preview mode and receiving constant improvements with the following versions of Java.Only final variables can be used as case value. switch throw try.catch var while with switch La declaración switch evalúa una expresión, comparando el valor de esa expresión con una instancia case, y ejecuta declaraciones asociadas a ese case, así como las declaraciones en los case que siguen. Variables are not allowed to be used as case value.The data type of switch expression and case value must be the same.Duplicate case values are not allowed i.e.Object game 'Hockey' // It is not allowed String game 'Hockey' // It is OK. In order to use string, you need to consider the following points: It must be only string object. Pick one argument which you want and use it as the String in the switch. String in Switch Statement In Java 7, Java allows you to use string objects in the expression of switch statement. OR - More readable with clear separation of case statementsīelow listed are the rules to be followed while using Switch Statement. You can use switch with String also, however youre trying to use a String array. Case Statement having value type same as that of the Expression The syntax of the Switch Case Statement is as mentioned below. The traditional way of using Switch Statement supports fallthrough which can introduce bugs in case the programmer forgets to add an appropriate break statement. With the release of JDK 7, the expression works with Enums, String, and Wrapper classes. The Switch Case Statement can accept the expression as byte, short, char, and int primitive data types prior to JDK 7. The remaining sections of this tutorial explain using Switch Case in both the traditional way and the new approach via expressions. Java 13 has further enhanced it by introducing the keyword yield to output case results. Apart from the traditional way of using the Switch Case Statement, Java 12 also added options to use Switch Case via expressions which are going to make it easy to use it inline. There are few fallbacks in using the Switch Case Statement in the traditional way and Java 13 is introducing enhancements to its existing behavior of it. Almost all the programming languages support the Switch Case statement and Java is no exception to it.
Switch case java string code#
We can use the Switch Case statements to conditionally execute the code based on the result of the Switch Statement expression and the matching case to execute only a set of statements within the matched case.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
